The thing about setting a Land Speed Record is that speeding up is only half of the problem. Once you’ve gone flashing through the timing lights of the measured mile at over 1000 mph you are faced with stopping a heavy, very high speed vehicle in a limited distance (about 5½ miles on our chosen track on Hakskeen Pan in South Africa). 5½ miles sounds like a long way, but if you’re doing a mile every 3½ seconds, it doesn’t seem that far at all!
Just to make it slightly harder, the vehicle you’re in has (by design) as little aerodynamic drag as possible, so it will keep rolling for a long time...... Hence stopping the Car reliably is, perhaps, even harder than getting up to speed. After all, if we have any problems (e.g. a hydraulic leak, electrical problem, computer glitch) early in a run I always have the option of slowing down ahead of schedule, but once we hit 1000 mph, I must slow down in the distance remaining, regardless of any other problems.
With all of this in mind, we’ve got several ways to make sure that I don’t end up going cross-country in BLOODHOUND SSC at the end of a high-speed run. Stopping the Car means increasing the drag, so we are fitting airbrakes and 2 drag chutes – 3 different ways of slowing the Car. Once the car is down to about 200 mph (which will take about 4 miles), I can use wheel brakes to stop the Car in about half a mile – leaving us with a safety margin of one mile.... just in case!
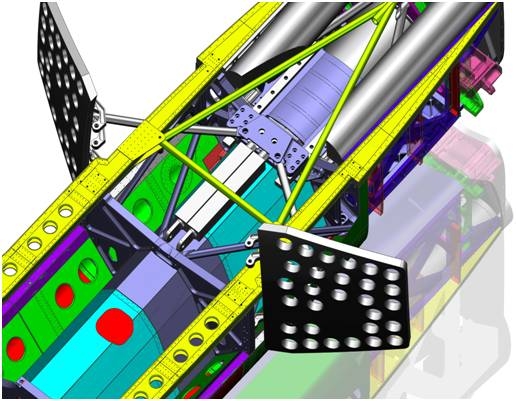
The airbrake design is now well advanced (picture top of page). The system uses 2 separate hydraulic rams, each with its own accumulator, to reduce the chances of a failure. We are getting a lot of great help from Parker on the system design and build, and at the same time LMS Samtech is doing a detailed stress analysis of the whole system. So far so good.
We’ve also been ‘crowd sourcing’ some elements of the airbrake design with engineering students at Lancaster University, who have been looking at the loads acting on the doors as they open.
Next up are the brake chutes. We’re using the same chutes as Thrust SSC used – not surprisingly, we need about the same amount of drag at the same speed. A 2-metre diameter ‘ring slot’ chute will give us 90kN (9 tonnes) of drag at Mach 0.9 (670 mph), which is just what we need to avoid going off the end of Hakskeen Pan. To keep the chutes away from the turbulence immediately behind the Car, we also need a 20 metre line, or ‘strop’, to attach the chute to the Car. With a 9 tonne working load, plus opening shocks of up to 50% above that, plus a 50% safety factor, that left us looking for a strop which will take about 20 tonnes – ouch.
 Marlow Ropes – stopping the world’s fastest diesel car
Marlow Ropes – stopping the world’s fastest diesel car
Step forward Marlow ropes, who make some of the best rope products in the world, and who also supplied the strops for both Thrust SSC and the JCB DIESLEMAX – so we’ve used their stuff before and we know that we can trust it.
For BLOODHOUND SSC, we will be using a 32mm diameter braided strop with a breaking strain of 23 tonnes. The strop will be 17 metres long (to start with at least – at its full working load of 9 tonnes, the strop will stretch by 3 metres, to a total length of 20 metres). Survival Equipment Services, our chute specialists, are now packaging a sample strop and chute into a deployment bag, so that we can check the fit in the limited space at the back of the Car. It should just go into the 1 metre by 250 mm space we have available. If it doesn’t, then I’m going to have to plead with the design office for a bit more room, or we’ll be pressure-packing all the chutes, which is hard work.
That just leaves the wheel brakes, which will be fitted to the front wheels only (the rear wheels are out in the airflow and rear brakes will create far too much drag at high speed). Here we have a bit of a problem. The brakes won’t be used at 1000 mph (they would melt almost immediately if they were), but they will still be turning at that speed, so we need some very strong brake discs if they are to survive the trip to 1000 mph and back. We have spent the past year or so looking for a carbon disc that will cope with this sort of spin speed, but we haven’t found a company that will make them for us.
 Not quite up to 1000 mph!
Not quite up to 1000 mph!
We even tested disc brakes from the RAF’s latest fighter, the Typhoon. I saw this aircraft doing amazing things over Libya last year, but it can’t quite manage 1000 mph at ground level – and neither can its brake discs (OK, it was a long shot, but we had to try!).
Back to square one – how are we going to stop the Car at the end of the track? The solution is a fairly simple one – use steel discs. Steel is not ideal for BLOODHOUND’s brakes as they will probably distort (and need replacing) if we use them a lot, but they are strong and cheap, so they will do the job. That solves the desert problem, but we’ll probably still be using carbon discs for the runway tests, as that’s one place where we will need a lot of braking. We are currently looking at commercial racing brakes, to see which package will best fit BLOODHOUND SSC.
 More great work from Lockheed Martin (UK)
More great work from Lockheed Martin (UK)
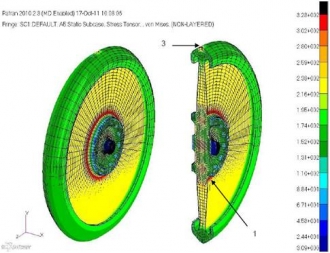
The development work on the rest of the Car is moving at a similarly rapid pace. We’re still looking at the details of wheel stresses, to make sure that the wheels can cope with the ride at 1000 mph – which induces loads of 50,000 ‘G’ at the wheel rim. To add to that, we have to allow for possible side loads (due to winds, or steering inputs) and even hitting a bump, as the tiniest of mounds in the track will have a significant effect at 1000 mph.
The good news is that the design works – Lockheed Martin (UK) has done some superb stress work for us, and results are indicating that we should have a 50% safety margin (which is the aerospace standard) at 1000 mph with a side load and a 4 ‘G’ bump. That sounds fine to me!
 Supersonic aero loads – a change is not as good as a rest
Supersonic aero loads – a change is not as good as a rest
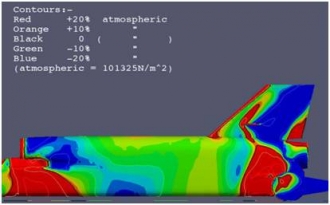
One thing we’ve discovered recently is a change in aerodynamic pressure across the rear wheels at high speeds. When BLOODHOUND SSC is travelling supersonic, the shock waves will exert a side load of over 200kg at the front of the wheel and a suction force of over 600kg at the rear. This would be fine if the wheel was stationary – but it will be spinning at 10,000 RPM, or 166 times per second.
That’s a load change of 800+kg trying to twist the wheel sideways 166 times per second. There is a risk of inducing a high-speed ‘wheel wobble’ – so we need to make sure that the wheel hub is strong enough to counteract this force. This level of modelling is real cutting-edge stuff, and we’ll find out more when we actually do it – it’s all part of the Engineering Adventure that is BLOODHOUND.
 Firing soon...
Firing soon...
Preparation for our first UK rocket firing continues, with the rocket test rig currently down at the BLOODHOUND Technical Centre in Bristol, being prepared for its trip to the test range shortly. As I said at the start of the year, these test firings are probably the major technical development challenge that we have in 2012, so we’re all very keen to get started.
Y  ou can never have too many access panels on a 13m long race car
ou can never have too many access panels on a 13m long race car
Vehicle integration is also receiving a lot of attention now. We are detailing the locations of all the access panels, refuelling, pressure charging and electrical connection points, and so on. Even individual bolts may need inspecting every day – for instance, the front suspension assembly fixes directly onto the cockpit monocoque, so rather than jack the Car up and remove the floor to check them, the best access may be for someone to go head-down into the cockpit each morning with a torque wrench to check that they are still secure. An important job, but I hope I don’t have to do it....
Funding this huge rate of activity continues to be a challenge, but even here things seem to be going well. We’ve been talking to several large companies in South Africa recently, and one of them phoned Project Director Richard Noble last week to ask for a formal sponsorship proposal. That’s always a good sign.
 Learning about the 1000mph Engineering Adventure in Northamptonshire
Learning about the 1000mph Engineering Adventure in Northamptonshire
The BLOODHOUND Education Programme is also going from strength to strength. Our recent tour of 100 Northamptonshire schools was a huge success and we’re now looking to make the relationship more permanent.
Across the country, we now have over 300 BLOODHOUND Ambassadors, with more in training. I met a team from Cisco at the start of the month, while they were doing their Ambassador training at the BLOODHOUND Technical Centre. They were all having fun and looking forward to passing on their new-found excitement about the science and technology of our Engineering Adventure. A big thank you to them, and to all of our other Ambassadors, for their help in inspiring the next generation of engineers.
The education programme is also developing strongly in South Africa. Dave Rowley, our former Education Director, is now based out there and is building up a strong following very quickly. The latest edition of Cisco BLOODHOUND TV features some of the education activity in South Africa.
Finally, a reminder that Bang Goes the Theory features BLOODHOUND on 30 April, when you’ll get to find out how presenter Dallas Campbell copes with the BLOODHOUND ‘G’ profile in an aeroplane. It’s the closest thing to actually driving the beast…. until next year, that is, when I get to do it for real!







